Pneumatic actuated valves use compressed air as the driving medium, and the resulting air pressure moves fluids safely and efficiently, directly affecting energy use, downtime, and safety. Choosing the right valve saves long-term costs. Focusing only on price is risky, as maintenance and failures may outweigh savings. This guide helps you select pneumatic valves that balance performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
1.Common Types of Pneumatic Actuated Valves
- Ball Valves – Fast on/off with excellent sealing. They quickly control flow in pipelines.
- Butterfly Valves – Lightweight, affordable, for large flow and low-pressure systems, e.g., HVAC or water treatment.
- Globe Valves – Accurate flow control for processes like chemical dosing.
- Gate Valves – For large pipelines, used in water, oil, and gas transmission.
- Check Valves – Prevent reverse flow, protecting pumps and equipment.

2.Key Factors in Pneumatic Valve Selection
- Control Needs – Use ball valves for fast shut-off in pipelines, such as emergency isolation lines. Engineers choose globe valves when they need precise flow control, for example in chemical dosing or mixing systems. For more technical insights on fluid dynamics in control systems, visit fyfluiddynamics.com.
- Pressure & Temperature – Use stainless steel or alloy valves in high-pressure steam lines or high-temperature process systems. This ensures durability and safety.
- Fluid Characteristics – Choose 316 stainless steel or coated valves for corrosive chemicals, abrasive slurries, or wastewater. Doing so prevents corrosion and wear.
- Operating Environment – Choose actuators and housings that operate reliably under varying air pressure conditions and withstand dust, humidity, or explosive environments.
- Cycle Frequency – High-cycle operations, such as frequent pump on/off sequences, require actuators capable of handling varying air pressure to ensure reliable operation. This helps reduce maintenance and downtime.
3.Material and Durability Considerations
- Aluminum – Low-cost, lightweight, suitable for mild environments.
- Stainless Steel (304/316) – Choose stainless steel to resist corrosion and ensure long service life, even at a higher initial cost.
- Carbon Steel – Strong, cost-effective for non-corrosive media.
- Special Alloys (Hastelloy, Monel) – Essential for corrosive or high-temp fluids.
- Seals (PTFE, Viton, EPDM) – Match to fluid type and temperature for durability and leak-free operation.
4.Compliance and Standards
- Follow ISO, API, CE, and UL standards to ensure valves meet strict safety, pressure, temperature, and leakage requirements. For detailed reference materials on industrial standards, see worddisk.com.
- Manufacturers test certified valves for reliability and ensure they are compatible with multiple systems. For example, API 6D valves are ideal for oil and gas pipelines, and UL-certified valves suit explosive environments.
- Standardized designs simplify maintenance, make spare parts readily available, and reduce downtime and repair costs.
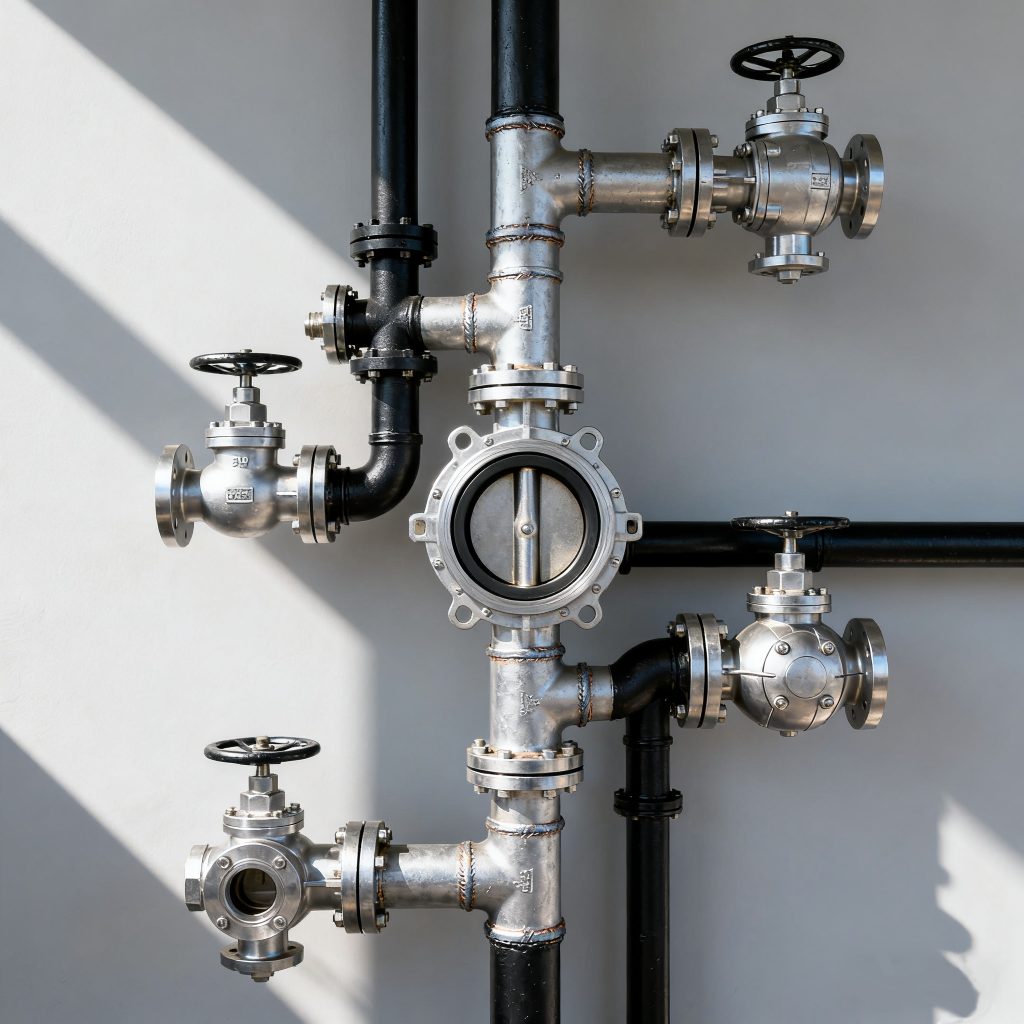

5.Cost vs. Value in Valve Selection
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including purchase, installation, maintenance, energy consumption, and expected lifespan.
- Install high-performance valves in critical areas. For example, use them in high-pressure steam lines or chemical dosing pipelines to ensure reliability and safety.
- In non-critical areas, choose economical valves. They are suitable for cooling water or general drainage systems and help reduce costs without affecting operation.
- Evaluate cost versus value to make smarter purchasing decisions that minimize long-term expenses.
6.Maintenance and Energy Efficiency
- Select valves that are easy to install and maintain while ensuring they meet system requirements.
- Choose actuators with low compressed air consumption to save energy without compromising performance.
- Ensure spare parts are available and compatible with your system.
- Consider smart valves with monitoring features for predictive maintenance, especially in critical applications.
7.Vendor and Market Considerations
- Select reliable suppliers with technical support and spare parts.
- Choose actuators based on system needs: pneumatic for fast cycles, electric for precision, hydraulic for high-force applications.
- Build long-term partnerships to reduce operational risks and ensure consistent performance.
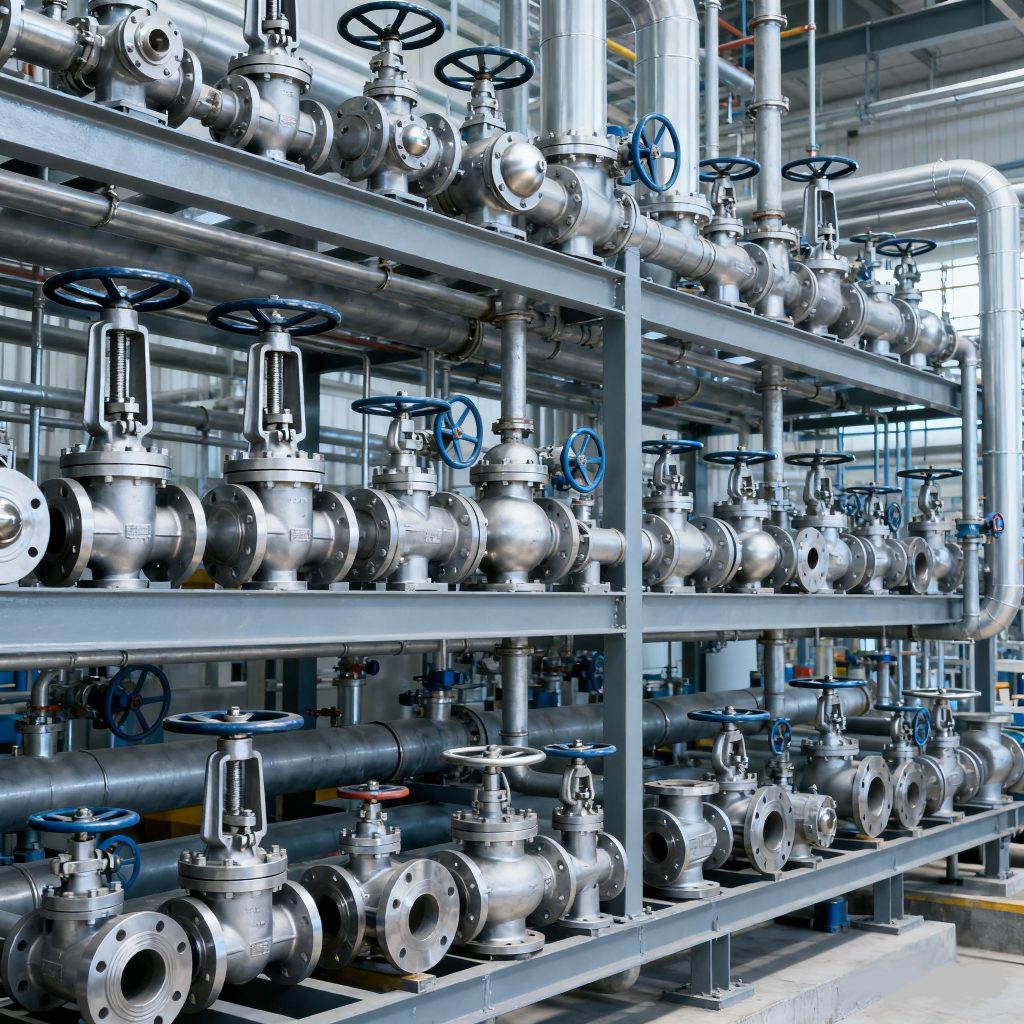

Conclusion
Selecting a valve is not just about price. A cost-effective solution balances performance, durability, material, compliance, energy use, and supplier reliability. Evaluating these factors ensures safer operations, lower energy costs, and long-term savings.
About Products
Interested in improving your flow control performance? Visit our Pneumatic Actuated Valve page for detailed insights and solutions.